Fluid Build up in the Lungs: Causes, Remedies, Prevention, and Risks
Fluid buildup in the lungs, also known as pulmonary oedema, is a serious condition that can significantly impact breathing and overall health. Understanding the causes, available treatments, prevention strategies, and potential dangers is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This article will explore pulmonary oedema in-depth, covering conventional and natural approaches to treatment and prevention.
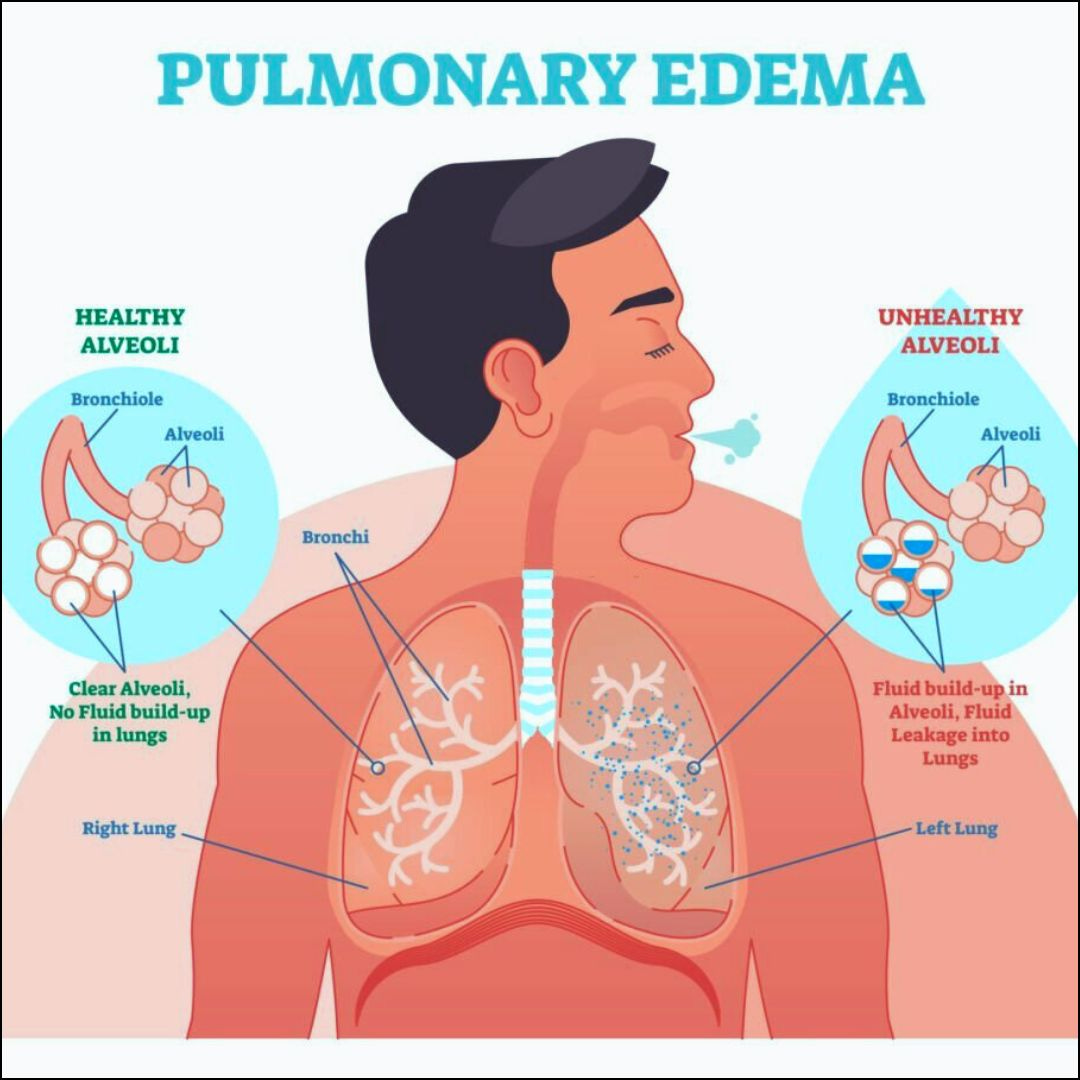
What is Pulmonary Oedema?
Pulmonary oedema occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. This fluid interferes with normal gas exchange, making it difficult for oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled. As a result, breathing becomes laboured and oxygen levels in the body can drop dangerously low.
Causes of Fluid Buildup in the lungs
There are two main categories of pulmonary oedema: cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic.
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Oedema:
This type is caused by heart problems, most commonly congestive heart failure. When the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently, pressure builds up in the blood vessels of the lungs, forcing fluid into the air sacs. Other heart-related causes include:
Heart attack
High blood pressure
Heart valve problems
Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
Non-cardiogenic Pulmonary Oedema:
This type is not directly related to heart function and can be caused by various factors, including:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Pneumonia
Sepsis (severe infection)
Kidney failure
Liver cirrhosis
High altitude exposure
Near-drowning
Inhalation of toxic substances
Severe allergic reactions
Certain medications
Trauma to the chest
Symptoms of Pulmonary Oedema
The symptoms of pulmonary oedema can develop suddenly (acute) or gradually over time (chronic). Common symptoms include:
Shortness of breath, especially when lying down
Difficulty breathing
Wheezing or gasping for air
Coughing, sometimes with pink, frothy sputum
Chest pain or tightness
Rapid, irregular heartbeat
Anxiety and restlessness
Blue-tinged lips or fingernails (cyanosis)
Excessive sweating
Fatigue
In severe cases, pulmonary oedema can lead to respiratory failure, requiring immediate medical attention.
Natural Remedies for Pulmonary Oedema
While pulmonary oedema often requires medical intervention, several natural remedies may help support lung health and alleviate symptoms. It's important to note that these should be used in conjunction with, not as a replacement for, conventional medical treatment.
Herbal Remedies:
Hawthorn: This herb may help strengthen the heart and improve circulation.
Garlic: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, garlic may help reduce fluid retention.
Dandelion: Acts as a natural diuretic, potentially helping to reduce fluid buildup.
Ginger: May help reduce inflammation and improve circulation.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Mohamed’s Health and Well- Being Substack to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.